Battle of Cabezón
| Battle of Cabezón | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Peninsular War | |||||||
 Flight of the Spanish at the Cabezon bridge | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Cuesta |
Lasalle Merle | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
300 regular cavalry 4,700 militia 4 guns[1] Total: 5,000 | 9,000 regulars | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 1000 dead[2] | 50 dead[3]/12 killed, 30 wounded[4] | ||||||


125miles
Madrid
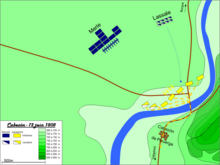
The Battle of Cabezón was an engagement early in the Peninsular War on 12 June 1808 between Spain's Army of Castile, under Cuesta, based at Valladolid, and detachments of Marshal Bessières' French Army Corps under generals General Lasalle[2] and Merle. Lasalle occupied Valladolid without opposition that same evening.[4]
Merle's column consisted of six battalions and two squadrons, while Lasalle's was made up of four battalions and two regiments of chasseurs.[4]
Cuesta's forces consisted of four cannon and 4,000 or 5,000 volunteers, who had not been more than a fortnight under arms, plus 300 cavalry, his only veteran troops.[4]
Battle[edit]
The battle took place at the bridge of Cabezon, where the main road from Burgos to Valladolid crosses the river Pisuerga.[4]
After scouting the Spanish position, Lasalle ordered General Sabatier to attack, while Merle cut the Spanish troops off from retreating to Valladolid. They stood the enemy's fire about 30 minutes, then began to flee, leaving behind 1000 dead and 4000 muskets. Cuesta, with the remains of his army, retreated to Leon.[2]
Aftermath[edit]
The guerilla war proceeded till the end of the Peninsular war.
The Spanish conventional warfare started with the Battles of El Bruch.
Oman (1902): A History of the Peninsula War, Vol. I[edit]
News had arrived that the captain-general, Cuesta, was collecting a force at Valladolid, which threatened to cut the road between Burgos and Madrid. To deal with him Bessières told off Merle, and another small column of four battalions and two regiments of chasseurs under his brilliant cavalry-brigadier, Lasalle, one of the best of Napoleon's younger generals. After sacking Torquemada (where some peasants attempted an ineffectual resistance) and ransoming the rich cathedral town of Palencia, Lasalle got in touch with the forces of Cuesta at the bridge of Cabezon, where the main road from Burgos to Valladolid crosses the river Pisuerga. On the eleventh of June Merle joined him: on the twelfth their united forces, 9,000 strong, fell upon the levies of the Captain-general.
Throughout the two years during which he held high command in the field, Gregorio de la Cuesta consistently displayed an arrogance and an incapacity far exceeding that of any other Spanish general. Considering the state of his embryo 'army of Castile', it was insane for him to think of offering battle. He had but four cannon; his only veteran troops were 300 cavalry, mainly consisting of the squadrons which had accompanied Ferdinand VII as escort on his unhappy journey to Bayonne. His infantry was composed of 4,000 or 5,000 volunteers of the Valladolid district, who had not been more than a fortnight under arms, and had seen little drill and still less musketry practice. It was absolutely wicked to take them into action. But the men, in their ignorance, clamoured for a battle, and Cuesta did not refuse it to them. His dispositions were simply astounding; instead of barricading or destroying the bridge and occupying the further bank, he led his unhappy horde across the river and drew them up in a single line, with the bridge at their backs.
On June 12 Lasalle came rushing down upon the 'army of Castile', and dashed it into atoms at the first shock. The Spanish cavalry fled (as they generally did throughout the war), the infantry broke, the bridge and the guns were captured. Some hundreds of the unfortunate recruits were sabred, others were drowned in the river. Cuesta fled westwards with the survivors to Medina de Rio Seco, abandoning to its fate Valladolid, which Lasalle occupied without opposition on the same evening. The combat by which this important city was won had cost the French only twelve killed and thirty wounded. (Oman, pp. 140–141.)[4]
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ Gates 2001, p. 71.
- ^ a b c Southey 1828, p. 455.
- ^ Gates 2001, p. 73.
- ^ a b c d e f Oman, Charles (1902). A History of the Peninsula War, Vol. I, pp. 140–141. Project Gutenberg. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
References[edit]
- Gates, David (2001). The Spanish Ulcer: A History of the Peninsular War. Da Capo Press. ISBN 0-306-81083-2.
- Southey, Robert (1828). History of the Peninsular War. Vol. I (New, in 6 volumes ed.). London: John Murray. Retrieved 6 May 2021.
External links[edit]
 Media related to Batalla de Cabezón at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Batalla de Cabezón at Wikimedia Commons
| Preceded by Capture of the Rosily Squadron |
Napoleonic Wars Battle of Cabezón |
Succeeded by First siege of Zaragoza |
