Tiburón Island Tragedy
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2018) |
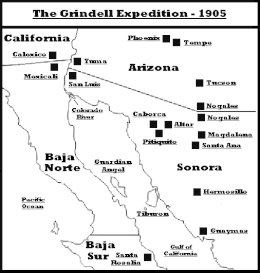
The Tiburón Island Tragedy, also known as the Grindell expedition, occurred in 1905 when three members of a small American gold prospecting expedition, led by Thomas F. Grindell, went missing in the Sonoran Desert near Tiburón Island (lit. "Shark Island"). At the time, Tiburón was inhabited by the Seri natives, nonetheless, Jack Hoffman, the only American survivor, testified that they were not responsible for the expeditioners' deaths.[1] The expedition, which expected to return by August 1905,[2] consisted of Grindell, who was an educator and former clerk for the Arizona Supreme Court,[2] Gus Olinder Ralls, D. Ingram and Hoffman, as well as their Tohono Oʼodham guide, Dolores Valenzuela.[1] The members of the expedition are believed to have perished from starvation and thirst based on Hoffman's report that Grindell had a single donkey carry all the water through the Sonora. When the equipment they were carrying to purify the water failed, Valenzuela split from the group, while the four men decided to continue and sought a boat to carry them to Tiburón. Hoffman spent four months alone, travelling 150 miles from Tiburón to Guaymas,[1] arriving "naked [and] blackened by the sun.[2]
Another expedition, led by Edward P. Grindell, who was Thomas's brother and wrote a piece based on his experience,[3][2] set off to find the remains of the expeditioners. Then-governor Rafael Izábal, approved Edward Grindell's quest, who recruited twelve Tohono Oʼodham scouts to search for Valenzuela, who was reportedly "afraid of the government," since it was considered an offense for "a guide [to return] without guiding [their] people back safely." The first clue appeared at Coyote Springs, New Mexico, followed by a campsite at one place "and another campsite farther in." They uncovered artefacts from the expedition, including a book on marine science belonging to one of the expeditioners, as well as the pack animal's corpses.[2] Additionally, the Arizona Rangers fruitlessly joined in the search, since "they had fought with Thomas Grindell with the Rough Riders."[2][4] On Monday, 25 December 1906 Thomas Grindell's corpse was found and it was confirmed that he had died from dehydration.[2][5] As Thomas's body was discovered, Edward could collect insurance,[5] however, this did not occur, due to the cost of the expedition ultimately outweighing the insurance money.[2] Valenzuela's body was never located,[1] leaving Hoffman, as the sole confirmed survivor.[6][7][5] [vague]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d Pesut, Ivan (27 December 2019). "The Tiburon Island Tragedy – What Happened?". World Atlas. Archived from the original on 1 December 2020. Retrieved 12 June 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Rooks, Fran (5 February 2020). "Was It Cannibals or the Desert That Killed the Explorers?". HubPages. Archived from the original on 13 June 2021. Retrieved 12 June 2021.
- ^ "The Wide World Magazine: An Illustrated Monthly of True Narrative, Adventure, Travel, Customs and Sport ..." A. Newnes, Limited. 12 September 1907. Retrieved 12 September 2022 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Arizona Rangers Thomas H. Rynning: A New Captain For Rangers:Tiburon Island Tragedy". Archived from the original on 16 September 2016. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ a b c "Google news: Boston Evening Transcript - December 27, 1906". Boston Evening Transcript. 27 December 1906. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ McClintock, James H. (1916). Arizona, prehistoric, aboriginal, pioneer, modern: the nation's youngest commonwealth within a land of ancient culture, Volume 2. The S. J. Clarke publishing co.
- ^ Grindell, Edward P. (1907). The Wide World Magazine: an illustrated monthly of true narrative, adventure, travel, customs, and sport, Volume 19: The Lost Explorers: The Mystery of a Vanished Expedition. G. Newness.
External links[edit]
- The Lost Explorers: The Mystery of a Vanished Expedition (1907) by Edward P. Grindell
