Operation Sportpalast
| Operation Sportpalast | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of World War II | |||||||
 Fairey Albacore aircraft taking off from HMS Victorious to attack Tirpitz on the morning of 9 March 1942 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
1 battleship 3 destroyers 8 submarines |
2 battleships 1 battlecruiser 1 aircraft carrier 1 cruiser 12 destroyers | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 1 aircraft |
2 aircraft 1 merchant ship 1 armed whaler | ||||||
Operation Sportpalast (German: Sports Palace), also known as Operation Nordmeer (German: Northern Sea), was a German naval raid between 6 and 13 March 1942 against two of the Allied Arctic convoys of World War II as they passed through the Norwegian Sea. It was conducted by the battleship Tirpitz, three destroyers and eight submarines. The German ships were unable to locate either of the convoys but sank a merchant vessel that was sailing independently. The Allies attempted to intercept the German force, also without success.
The operation was the first major German attack on the convoys that were travelling to and from the Soviet Union and used warships that had been transferred to occupied Norway in early 1942. Tirpitz and her escorts sailed on 6 March. The Allies learned of this from decoded German radio signals, and the British Home Fleet attempted to locate and destroy the German force. This intelligence was also used to re-route the convoys to evade Tirpitz. The British located the German battleship on the morning of 9 March, by which time she was returning to Norway. An attack against Tirpitz by torpedo bombers flying from the aircraft carrier HMS Victorious failed and two British aircraft were shot down. The German ships returned to their base on 13 March.
The British were disappointed with their failure to damage or sink Tirpitz. This was attributed to shortcomings with the aircraft and tactics used. They believed that the battleship posed a significant threat to the convoys, leading to strong escorts being assigned to them. The German Navy was chastened by how close Tirpitz came to disaster and decided to be more cautious. The battleship was only dispatched against one other convoy, PQ 17 in June 1942 and was recalled before attacking it. She was subjected to many attacks at her anchorages in Norway and finally sunk in November 1944.
Background[edit]
Before the outbreak of World War II the Kriegsmarine (German Navy) developed plans to attack Allied merchant shipping in the event of war. The navy's commander, Grand Admiral Erich Raeder, believed that battleships and cruisers were a key part of this strategy. As a result, the Scharnhorst and Bismarck-class battleships that were constructed in the late 1930s and early 1940s were designed to be capable of making long range anti-shipping raids into the Atlantic Ocean.[1] Tirpitz was the second of the two Bismarck-class vessels and was launched in April 1939 and commissioned on 25 February 1941.[2]
The Kriegsmarine made two battleship raids against Allied convoys in the Atlantic Ocean during early 1941. The battleships Gneisenau and Scharnhorst conducted Operation Berlin between January and March 1941. During this raid they sailed from Germany, attacked Allied shipping and returned to occupied France. A second raid, Operation Rheinübung, was attempted in May and involved the battleship Bismarck and heavy cruiser Prinz Eugen. While the German ships destroyed the British battlecruiser HMS Hood on 24 May, Bismarck was crippled by Fairey Swordfish torpedo bombers from the British aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal and sank on 27 May after being bombarded by several British battleships from the Home Fleet. Admiral Sir John Tovey was the commander in chief of this fleet, and led it from the battleship HMS King George V during the battle.[3][4] The loss of Bismarck left Tirpitz as Germany's only remaining full-sized battleship. At the time her crew were still being trained.[5]

After the German invasion of the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941 the Allies began sending convoys loaded with supplies through the Norwegian Sea and Arctic Ocean to ports in northern Russia. The Arctic convoys that were dispatched during 1941 and early 1942 were lightly opposed, with only a single Allied merchant ship and the destroyer HMS Matabele being sunk by German submarines prior to March 1942.[6][7] Harsh weather conditions, including extreme cold, heavy seas and gales, made air and naval operations in the area difficult for all of the combatants.[8]
In December 1941 the German military began transferring substantial naval and air forces to northern Norway, which they had occupied since early 1940. The forces sent to Norway were tasked with attacking the Arctic convoys as well as defending the area from an invasion. At this time the German dictator Adolf Hitler wrongly believed the Allies intended to invade Norway.[9] On 12 January 1942 Hitler ordered Tirpitz to be transferred from Germany to Trondheim in Norway. The battleship and two escorting destroyers departed Wilhelmshaven in Germany on 14 January and arrived in Trondheim on 16 January.[10] She was to form the main element of a powerful battle group once other German warships arrived in the area.[11] Kapitän zur See Karl Topp commanded Tirpitz at this time.[5]
The Allies learned of Tirpitz's arrival at Trondheim on 17 January from Ultra intelligence obtained by decrypting intercepted German radio signals.[12] British photo reconnaissance aircraft located the battleship there on 23 January, and regular sorties were flown over the Trondheim area to monitor her.[13] Due to the threat Tirpitz posed to Allied convoys in the Atlantic Ocean and Norwegian Sea, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill directed on 25 January that "the destruction or even crippling of this ship is the greatest event at sea at the present time. No other target is comparable to it".[14] The Royal Air Force (RAF) dispatched 16 heavy bombers to attack Tirpitz at its anchorage at on the night of 29/30 January, but no damage was inflicted.[15] No. 217 Squadron RAF was also ordered in February to prepare for a one-way mission against the battleship. This would have involved its Bristol Beaufort aircraft making an attack and the crews then parachuting over neutral Sweden or ditching into the sea. The raid was not attempted, and No. 217 Squadron returned to normal duties in mid-March 1942.[16]
Allied intelligence learned that Tirpitz was undertaking training in Trondheim Fjord on 19 February. In response, Tovey sailed that day with most of the Home Fleet to either raid the Norwegian port of Tromsø or attack Tirpitz if she put to sea.[15] He cancelled the raid on Tromsø after the Admiralty passed on intelligence that another group of German ships was being transferred to Trondheim; these were the heavy cruisers Admiral Scheer and Prinz Eugen with three destroyers. The aircraft carrier HMS Victorious, escorted by the heavy cruiser HMS Berwick and four destroyers, was detached to attack these ships and four submarines took up positions near Trondheim. The carrier's aircraft were unable to locate or attack the German force due to bad weather, but the submarine HMS Trident torpedoed and badly damaged Prinz Eugen near the entrance to Trondheim Fjord on 23 February. Admiral Scheer was undamaged, and anchored near Tirpitz.[17][18] The Admiral Commanding Battleships, Vice-Admiral Otto Ciliax, assumed command of this battle group and used Tirpitz as his flagship.[19][20] Ciliax had led the German forces in the Channel Dash between 11 and 13 February, during which Gneisenau, Scharnhorst and Prinz Eugen returned to Germany from Brest, France, via the English Channel. Both battleships were damaged by mines during this operation, and were unable to be dispatched to Norway as intended. While the failure to prevent the battleships from passing through the English Channel was intensely embarrassing to the British, the German redeployment ended the threat which the warships at Brest had posed to Allied shipping in the Atlantic.[21]
Prelude[edit]
Allied convoys[edit]

Due to the presence of the battle group at Trondheim, the Home Fleet was directed to provide a powerful distant covering force for the next Arctic convoys; this was the first time that this had been done. The British also stepped up their air patrols of the Trondheim area and Norwegian Sea to monitor German naval movements. Two Arctic convoys sailed simultaneously on 1 March 1942. PQ 12 left Iceland bound for the Soviet Union, and QP 8 departed Murmansk in northern Russia to return ships to the Atlantic. PQ 12 was made up of 17 merchant ships and was escorted by a heavy cruiser, 2 destroyers and several armed Norwegian whalers.[20][22][23] QP 8 comprised 15 merchant vessels and had a weak escort of 2 corvettes and 2 minesweepers.[24] Tovey had requested that the convoys sail simultaneously to make it easier for the Home Fleet to protect them while they passed through the waters between Jan Mayen and Bear Islands where they would be at greatest risk of attack by German surface ships.[25]
On 3 March a force under the Home Fleet's deputy commander Vice-Admiral Alban Curteis departed Iceland to protect the convoys. It comprised the battleship HMS Duke of York, battlecruiser HMS Renown and six destroyers.[26] Tovey was on board King George V at the fleet's main base at Scapa Flow. He preferred to remain there with the battleship and Victorious to remain in contact by telephone with his sources of intelligence and intercept Tirpitz if she attempted to break out into the Atlantic.[20] Retaining part of the fleet at Scapa Flow would also help to keep ships and their crews combat ready over what was anticipated to be a lengthy campaign, with Tovey believing that Gneisenau and Scharnhorst would join Tirpitz over the summer after they were repaired.[27][28] The Admiralty disagreed with this strategy and ordered Tovey to put to sea on 3 March so that the full force of the Home Fleet could be brought to bear against Tirpitz if she sailed.[29] In doing so it accepted responsibility for the consequences if the German battleship entered the Atlantic.[20] Tovey sailed shortly afterwards with King George V, Victorious, Berwick and six destroyers.[26] The two main elements of the Home Fleet met up to the east of Jan Mayen on 6 June.[20] Tovey was under orders to give precedence to protecting the convoys over destroying Tirpitz. He was unhappy with this, and regarded the sinking of the battleship as being of "incomparably greater importance to the conduct of the war than the safety of any convoy".[30] The forces under Tovey's command were considerably more powerful than those available to Ciliax.[31]
Victorious's air wing included two squadrons equipped with Fairey Albacore torpedo bombers, 817 and 832 Naval Air Squadrons.[32] The number of Albacores assigned to the squadrons differed; 817 Squadron had nine and 832 Squadron twelve.[33] These obsolescent biplanes could be armed with a single torpedo and were slow and unmanoeuvrable. The crews of the two Albacore squadrons were experienced, but had received little training in attacking enemy warships.[34][35][36] The other element of the carrier's air wing was the Fairey Fulmar fighter-equipped 809 Naval Air Squadron.[33] The Fulmars were inferior to German fighters due to their lack of speed and manoeuvrability, but were capable of intercepting bombers.[37] Tovey regarded the amount of air support available to his fleet as inadequate.[28]
German plans[edit]
The crew of a German Focke-Wulf Fw 200 Condor maritime patrol aircraft sighted ships of PQ 12 near Jan Mayen at around noon on 5 March. The commander of the German Naval Group North, General Admiral Rolf Carls, requested permission to attack the convoy using Ciliax's force. This was granted by Raeder after he consulted with Hitler.[26] Raeder's orders for Ciliax specified that he was to avoid Allied naval forces to the extent possible, and only attack convoys if they were protected by an equal or lesser force than his own.[38] The raid is usually called Operation Sportpalast by historians, but was designated Operation Nordmeer by Ciliax and his staff.[39]
Ciliax was aware that two Allied convoys were at sea. While he believed that they would be protected by the Home Fleet, he did not know its strength or whether it had sailed. His plan for the operation was to intercept one or both of the convoys in the area between Jan Mayen and Bear Island.[40][41] Once a convoy was encountered, Tirpitz was to destroy its escorts and then she and the destroyers would attack the cargo ships.[42] Due to fuel shortages, Ciliax was unable to sail with his entire force. He departed Trondheim at noon on 6 March with Tirpitz and the destroyers Friedrich Ihn, Hermann Schoemann and Z25.[38][40]
Eight German submarines based in Norway were assigned to support Tirpitz. The four submarines with the most experienced crews were positioned in locations where it was hoped they could attack the Home Fleet if it intervened. The other four submarines operated near Murmansk to attack any ships from PQ 12 that escaped the battleship.[43]
Battle[edit]
6–7 March[edit]

The German ships were not spotted by Norwegian resistance agents as they departed.[38] The scheduled British photo reconnaissance flight over Trondheim was unable to be conducted on 6 March due to bad weather, and the additional air patrols over the Norwegian Sea that were meant to be conducted in this eventuality were not flown due to a shortage of aircraft. Contact was first made by the submarine HMS Seawolf at 6:01 pm on 6 March, with its crew spotting a single large warship while patrolling north of the exit to Trondheim Fjord. Seawolf's commanding officer Lieutenant Dick Raikes assumed this was Tirpitz. He attempted to attack the German force, but was outpaced and broke off. Seawolf's crew then sent a radio report of this contact, which indicated that the ship was either a cruiser or a battleship.[38][44] The German battle group sailed north-east along the coast of Norway at 23 knots (43 km/h; 26 mph) for the remainder of 6 March and turned north at midnight.[45]
During 6 March PQ 12 passed through areas of loose pack ice. This forced it to take a south-easterly course for much of the day, and resulted in serious damage to the destroyer HMS Oribi.[46] QP 8 was also behind schedule, as it had been scattered by gales on 4 and 6 March. The Soviet cargo ship Izhora and the American vessel Larranga fell behind the convoy on 4 March and were unable to rejoin it.[47]
Tovey received Raikes's report shortly after midnight on the night of 6/7 March, and judged that Tirpitz was at sea. He believed that the battleship was probably being used to protect northern Norway from a landing, but was unable to discount the possibility that she would attack the convoys.[44] Tovey wanted to use Curteis's force to protect the convoys while the ships under his direct command intercepted Tirpitz. The Admiralty refused to permit this and directed the Home Fleet to remain concentrated so that Victorious's fighters could protect it from air attack.[48] Tovey ordered the fleet to sail to the north to reach a position from which Victorious could launch search aircraft at 10 am. Icy conditions at that time made flying impossible, however. This was a missed opportunity for the British, as the planned search was highly likely to have located Tirpitz at a time when the Home Fleet was less than 100 miles (160 km) from her.[19][44]
The Germans lacked information on the location of PQ 12, as their aircraft and submarines had failed to spot the convoy again. Ciliax was still unaware that the Home Fleet was operating near his ships.[41] Tirpitz flew off two Arado Ar 196 float planes on the morning of 7 March, but they did not find PQ 12. Ciliax also detached the three destroyers to undertake independent searches.[49] Weather conditions remained bad throughout the day, with frequent squalls and blizzards. The two convoys passed one another in the afternoon. Z25 came within 10 miles (16 km) of QP 8 but did not sight it.[50] During the afternoon of 7 March the Admiralty warned PQ 12 that German ships might be operating in its vicinity. In response, the convoy temporarily altered its course to the north before turning east again to avoid an area of sea ice.[51][47]
At around 4:30 pm Friedrich Ihn spotted the Izhora. Tirpitz changed course to join the destroyer. Friedrich Ihn attacked and hit Izhora with a torpedo, but the cargo ship's radio operator managed to send a sighting report before it sank. This was received by the Home Fleet, giving Tovey an approximate location for the German force.[50] The British also intercepted a radio transmission from a German submarine at 4:40 pm which was wrongly identified as having been sent by Tirpitz. Radio direction finding indicated that this transmission had been sent from near PQ 12, and Tovey issued orders for six of his destroyers to detach and search the route that the German ships might be using to return to Norway from Izhora's position while the main battle fleet proceeded to the north-east to protect the convoy. Tovey received Ultra intelligence that afternoon which confirmed that the Germans were hunting the convoys rather than seeking to prevent an Allied landing.[52][53] Another radio signal from a German submarine that was intercepted at 7:40 pm led Tovey and his staff to wrongly believe that Tirpitz was rapidly sailing south.[54]
Ciliax continued to search for the convoys during the afternoon of 7 March. His destroyers ran low on fuel, and Friedrich Ihn was detached to refuel in Narvik and then rejoin the battle group. Two attempts to refuel the other destroyers from Tirpitz failed due to bad weather, and they were sent to Tromsø instead.[55] The battleship suffered mechanical problems on 7 March that could not be repaired at sea. This limited her speed to 29.5 knots (54.6 km/h; 33.9 mph).[56]
8 March[edit]
The six British destroyers proceeded to the south-east, before turning north at 2 am on 8 March. They failed to spot any of the German ships. At this time Tirpitz was searching for the convoys independently and was approximately 250 miles (400 km) north-east of the Home Fleet.[53][54][55] The British destroyers were low on fuel after their search, and headed for Iceland to refuel. This left the Home Fleet with only a single destroyer, as two had been detached to refuel in Iceland the previous night.[57] Tovey judged that the German battleship had evaded his destroyers, and turned to the south-west to meet up with other destroyers that were needed to protect the capital ships from submarines.[54] He received further Ultra intelligence about German aircraft operations and appreciations of British radio activity during the morning and shortly after noon, but in a blunder this advice failed to note that the intercepted radio signals were addressed to Ciliax. Had Tovey been informed of this, it is likely that he would have concluded that Tirpitz was not headed to Norway and turned the Home Fleet around.[58]
During the morning of 8 March, Tirpitz headed north towards Bear Island in an attempt to get ahead of PQ 12. The battleship then turned to the south-west on a course which Ciliax believed would intercept the convoy and her crew were called to action stations ahead of the expected battle. Ciliax was mistaken, as PQ 12 had changed its course at dawn after being warned of the attempted interception by intelligence sourced from Ultra. It passed to the north of Tirpitz. The battleship and a patrolling Condor did not spot any of the Allied ships.[59][60][61] Naval Group North sent Ciliax a signal at 6:20 pm that suggested that PQ 12 might have abandoned its voyage after being spotted on 5 March and gave him permission to break off the operation if he wished. Ciliax decided to do so, and at 8:25 pm turned south bound for Norway.[62]
Tovey received further Ultra intelligence during afternoon of 8 March that confirmed that Ciliax was operating in the Bear Island area. In response, he reversed the Home Fleet's course at 6:20 pm to head for Bear Island. It was taking only two or three hours at this time for intercepted German naval radio signals to be decoded, which allowed the forces at sea to rapidly respond to this intelligence.[58]
After changing course, Tovey broke radio silence to report to the Admiralty that he was heading north with the main body of the fleet and lacked protection against submarines. He also requested that the Admiralty assume direct control of the Home Fleet's separate forces of cruisers and destroyers given that it had a better understanding of their locations and could more easily communicate with them. Two cruisers had been sent into the Norwegian Sea, where they were operating near Jan Mayen. Another pair of cruisers and three of destroyers that had conducted the search on the morning of 8 March subsequently sailed from Iceland to patrol the same area. Groups of destroyers were also readied at bases in Iceland and Scotland to join the Home Fleet.[63] Tovey was hopeful that the Germans would intercept his radio signal and recall Tirpitz as this would guarantee the safety of PQ 12 and possibly bring the battleship within range of Victorious's aircraft.[62]
Morning of 9 March[edit]
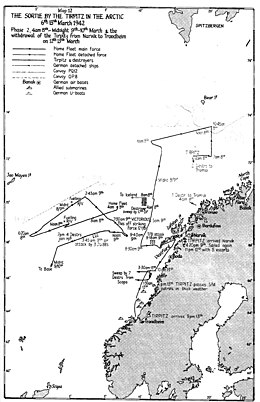
At 1:37 am on 9 March the Admiralty directed Tovey to "steer 120 degrees maximum speed". This was in response to an intercepted German radio message which revealed that Ciliax was headed to the Lofoten islands to meet up with destroyers there at 7 am that day. The Home Fleet adjusted its course to head for the Lofoten islands at 2:42 am at a speed of 26 knots (48 km/h; 30 mph).[63][64] At this time the British ships were about 200 miles (320 km) west of the German battleship.[35] Tovey received further Ultra intelligence during the early hours of the morning that confirmed the Germans were returning to Trondheim and provided Tirpitz's expected position at 1 pm that day.[64] A detachment of B-Dienst signals intelligence personnel on board Tirpitz intercepted radio signals from the Home Fleet, and warned Ciliax that a British force that included an aircraft carrier was in the area.[63]
By this time it was too late for the Home Fleet's battleships and battlecruiser to intercept the German force before it reached the Norwegian coast. There was a possibility though that Victorious's torpedo bombers could damage Tirpitz and slow the battleship down sufficiently to allow the Home Fleet to destroy her.[65] At 3:16 am Tovey requested that the aircraft carrier's commanding officer, Captain Henry Bovell, provide him with proposals for such an attack. Bovell responded with a plan to fly off six Albacores at 6:30 am to search for the Germans, followed by a strike force of twelve torpedo-armed Albacores an hour later.[66]
The six search aircraft were launched at 6:40 am; three were drawn from each of the two Albacore squadrons. At this time the Home Fleet was 115 miles (185 km) to the north-west of Tirpitz, which had rendezvoused with Friedrich Ihn.[66] Weather conditions were good.[63] The German force was spotted by the pilot of an Albacore at 8:03 am. As soon as the sighting report was received, the twelve strike aircraft were ordered to take off. Tovey sent a message to their crews stating that they had "a wonderful chance which may achieve the most valuable results".[66] The search aircraft maintained contact with Tirpitz. After they were spotted, Ciliax judged that a torpedo bomber attack was imminent. He ordered the battleship to full speed, directed that the crew take up their action stations and had her floatplanes launched. Only one of the float planes could be launched, and once it was in the air Ciliax changed the battleship's course to proceed to Vestfjorden so that she should shelter at Narvik.[67] At this time the battleship was only 50 miles (80 km) from the Norwegian coast.[68] Tirpitz's anti-aircraft guns fired on the search aircraft without success, but the float plane damaged one of them and wounded a crewman. The other search aircraft were not deterred, and continued to track the German ships.[67] Ciliax requested that the Luftwaffe (German air force) units in Norway provide fighter aircraft to protect his force, but it took several hours for any to be dispatched from nearby airfields.[69]

The British strike force was organised into four sub-flights, each with three Albacores, and was led by Lieutenant Commander Bill Lucas from 832 Squadron. Lucas had only recently joined the squadron and had no training in attacking enemy warships.[70] He spotted the German ships at 8:40 am, and ordered his command to approach them at an altitude of 3,500 feet (1,100 m) where scattered cloud might hide the aircraft from sight. Due to a strong easterly wind and the German ships' fast speed, the Albacores' closing speed was only 30 knots (56 km/h; 35 mph). British torpedo bomber doctrine called for strike forces to overtake their targets, and then have half the aircraft attack from the port and the others from the starboard with the torpedoes being released simultaneously between 800 yards (730 m) and 1,000 yards (910 m) from the enemy ships. Such an attack would be difficult for large warships to evade. Due to the slow closing speed, Lucas instead ordered each sub-flight to attack independently.[71]
The first attack was made by the sub-flight under Lucas's personal control. The aircraft approached Tirpitz from her port side and released their torpedoes at 9:18 am from a very low altitude and a distance that was probably greater than 1,000 yards from the battleship. Tirpitz turned sharply to port, and evaded these torpedoes. A sub-flight from 817 Squadron then made a similar attack from the port side of the battleship, with their torpedoes also missing.[72]
Tirpitz's manoeuvring forced the other two sub-flights to attack from astern rather than from starboard as their commanders had intended.[72] This required their crews to fly into heavy gunfire. They released their torpedoes at extreme range,[73] and two Albacores were shot down by Tirpitz's anti-aircraft gunners;[74] all six airmen aboard the aircraft were killed. No hits were achieved, though a torpedo came within 10 yards (9.1 m) of the battleship. Following this attack the British aircraft returned to Victorious, and landed at around 11:00 am.[73]

The German sailors were relieved to have escaped the British attack without any damage being inflicted on Tirpitz. Their only casualties were three men who had been wounded by gunfire from the British aircraft. Ciliax awarded Topp the Iron Cross on the spot for his skill in evading the British torpedoes.[73] The surviving British airmen were berated by Victorious's senior officers when they were debriefed.[75] In his report, Bovell criticised Lucas for beginning the attack before his aircraft were in the proper position and judged that the other pilots had released their torpedoes at too great a distance from the battleship.[76][77] Tovey did not attempt a second torpedo bomber attack on Tirpitz as Victorious's aircraft were unable to operate in the defended airspace around Narvik with any prospect of success.[78]
9–13 March[edit]
The failure of the torpedo bomber attack meant that the Home Fleet was unable to bring Tirpitz to battle before she reached safety.[35] The German battleship anchored near Narvik at 8 pm on 9 March.[76] In the late afternoon of 9 March the Home Fleet turned to the west to evade possible German air attacks. German reconnaissance aircraft began shadowing the fleet, but none of Victorious's Fulmar fighters were flown off as it was thought that they would be unable to intercept them. At 3:45 pm three German Junkers Ju 88 aircraft unsuccessfully attacked the Home Fleet with bombs. Four destroyers joined the Home Fleet at around 7 pm. Tovey considered raiding German positions in Norway, but decided against this and instead set course for Scapa Flow. The Home Fleet, which had been reinforced with a further eight destroyers, arrived at Scapa Flow at night on 10 March.[78]
On 9 March HMS Shera, one of two armed Norwegian whalers that had been dispatched from Iceland to strengthen PQ 12's escort, capsized while searching for the convoy. Only three members of her crew were rescued by the other whaler, which then proceeded directly to Murmansk.[46][79]
Tirpitz's crew completed repairs to the battleship's engines 48 hours after her arrival at Narvik.[80] She departed the port with an escort of five destroyers just before midnight on 12 March. Guided by Ultra intelligence and reports from resistance agents in Norway, a force of eight British destroyers under the command of Captain Alan Scott-Moncrieff attempted to intercept the German force between Trondheim and Bodø that night. They did not make contact, and were forced to turn away from the coast at 3:30 am to avoid being attacked by German aircraft once dawn broke. Four British submarines stationed along the route between Narvik and Trondheim were also unable to attack the German ships. Tirpitz anchored near Trondheim at 9 pm on 13 March.[81][82] The British received reports of her arrival there from Norwegian agents and these were confirmed by a photo reconnaissance aircraft on 18 March.[64][83]
Both convoys reached their destinations without further loss.[84] QP 8 arrived at Reykjavík in Iceland on 11 March.[85] Most vessels of PQ 12 reached Murmansk on 12 March, but several that had become separated from the convoy arrived in Russian ports on other dates. One of the Norwegian whalers assigned to PQ 12 shot down a German aircraft while it was attempting to bomb a merchant ship on 13 March. This was the only attack on the convoy during its voyage.[27][79] Two of the four German submarines that were operating off Murmansk spotted ships from PQ 12 as they approached the port, but neither was able to attack.[86]
Aftermath[edit]
Assessments[edit]
The British were disappointed by their failure to sink or damage Tirpitz.[35] Following the operation Tovey was critical of the instructions he had received from the Admiralty. He believed that the order to prioritise the defence of the convoys over attacking the battleship had hindered his operations and that the fleet should not have been sent into waters where large numbers of submarines were operating as it lacked enough destroyers to protect its capital ships. He was also frustrated by the Admiralty's attempts to closely manage his command during the battle. The Admiralty conceded the first two of Tovey's criticisms, agreeing that sinking Tirpitz would be the Home Fleet's main priority when it covered convoys in the future and that the fleet should not proceed beyond 14 degrees east if it lacked destroyers. His other criticism was thought to be unfair as the Admiralty had better access to Ultra intelligence than Tovey did while at sea.[30][87]
On 13 March Churchill asked the First Sea Lord, Admiral of the Fleet Sir Dudley Pound, to provide "a report on the air attack on TIRPITZ, explaining how it was that 12 of our machines managed to get no hits as compared to the extraordinary efficiency of the Japanese attack on PRINCE OF WALES and REPULSE". The reason was that Japanese had enough highly effective aircraft with well trained crews while the Fleet Air Arm did not.[88] Pound attempted to explain this to Churchill, but the Prime Minister was not fully convinced and it contributed to him becoming sceptical about the value of the Fleet Air Arm.[89] Nevertheless, the failure of the attack on 9 March led to a decision to accelerate improvements to the Royal Navy's aviation force.[88]
Operation Sportpalast also demonstrated the threat which the German warships in Norway posed to the Arctic convoys, and it was also decided that the Home Fleet would cover them all in the future. This prevented ships being transferred from the fleet to other theatres of the war.[84] Pound was so concerned about the risk of Tirpitz attacking an Arctic convoy that he sought Churchill's agreement to not dispatch any of them during the period of summer in which there would be almost continuous daylight in the Arctic. The Prime Minister did not agree.[90] In contrast, Tovey believed that the Germans would be cautious with how Tirpitz was used as a result of their experiences during Operation Sportpalast. He expected that they would not assign her to attack convoys while they were passing through the Barents Sea.[87][91]
The Germans were chastised by Operation Sportpalast. Both Ciliax and Raeder believed that good luck was the only reason that Tirpitz had escaped damage or destruction.[84] As a result, Raeder and Hitler decided to only dispatch the battleship against convoys again if victory was considered certain.[92] Hitler also directed that she could only be used to attack convoys if it was first confirmed that no aircraft carriers were present.[93] Tirpitz was thereafter mainly held in reserve to attack Allied forces that attempted to make a landing in Norway. The other warships, as well as submarines and aircraft, were used against the convoys.[30][92] As a result, the Allies had no opportunities to attack Tirpitz at sea after Operation Sportpalast.[76] RAF heavy bombers made further attacks against the battleship at Trondheim on 31 March and 28 and 29 April 1942, but did not inflict any damage.[94]
Subsequent operations[edit]
In June 1942 Raeder decided to dispatch Tirpitz and three heavy cruisers against the next Arctic convoy in what was designated Operation Rösselsprung.[95] This force sailed on 2 July after Convoy PQ 17 was detected bound for the Soviet Union, and put in at Altafjord in the far north of Norway on 4 July to await Hitler's permission to attack.[96][97] After learning Tirpitz had sailed Pound ordered the convoy to scatter and its escort to withdraw on the evening of 4 July, a decision Tovey strongly disagreed with. This led to heavy losses from German submarines and aircraft over subsequent days.[98][99] The battleship departed Altafjord on 5 July to attack the convoy, but was recalled by Raeder that night after it was learned that Victorious was at sea.[98][100]
Allied forces attacked Tirpitz at her anchorages in Norway during 1943 and 1944. The battleship was badly damaged on 22 September 1943 by the Operation Source raid which used midget submarines, and was never fully combat worthy again. The Fleet Air Arm inflicted further damage during the Operation Tungsten raid on 3 April 1944, but several subsequent carrier attacks failed due to bad weather and the continuing shortcomings of British naval aircraft. RAF heavy bombers crippled Tirpitz on 15 September 1944 during Operation Paravane, and sank her with considerable loss of life on 12 November that year.[101]
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ Konstam 2021, pp. 8–11.
- ^ Chesneau 1980, p. 224.
- ^ Konstam 2018, p. 30.
- ^ Correll 2017.
- ^ a b Konstam 2018, p. 31.
- ^ Hinsley 1981, pp. 199–200.
- ^ Woodman 2004, pp. 58, 67.
- ^ "A 5-Minute History of Arctic Convoys". Imperial War Museums. Retrieved 7 August 2021.
- ^ Hinsley 1981, p. 200.
- ^ Roskill 1956, p. 116.
- ^ Konstam 2018, p. 25.
- ^ Sweetman 2000, p. 12.
- ^ Sweetman 2000, pp. 13, 19.
- ^ Sweetman 2000, pp. 14–15.
- ^ a b Roskill 1956, p. 117.
- ^ Sweetman 2000, p. 18.
- ^ Roskill 1956, pp. 118–119.
- ^ Rohwer 2005, p. 146.
- ^ a b Roskill 1956, p. 120.
- ^ a b c d e Hinsley 1981, p. 205.
- ^ Roskill 1956, pp. 149–161.
- ^ Bishop 2012, pp. 68–69.
- ^ Woodman 2004, pp. 67–68.
- ^ Woodman 2004, pp. 67, 72.
- ^ Woodman 2004, p. 67.
- ^ a b c Bishop 2012, p. 69.
- ^ a b Faulkner 2012, p. 109.
- ^ a b Kemp 1999, p. 28.
- ^ Kemp 1999, pp. 28–29.
- ^ a b c Roskill 1956, p. 124.
- ^ Zetterling & Tamelander 2009, p. 26.
- ^ Bishop 2012, p. 71.
- ^ a b Brown 2009, p. 19.
- ^ Konstam 2018, p. 38.
- ^ a b c d Roskill 1956, p. 122.
- ^ Bishop 2012, pp. 72–73.
- ^ Barber 2008, p. 26.
- ^ a b c d Bishop 2012, p. 70.
- ^ Zetterling & Tamelander 2009, p. 333.
- ^ a b Konstam 2018, p. 33.
- ^ a b Kemp 1999, p. 31.
- ^ Zetterling & Tamelander 2009, p. 25.
- ^ Blair 2000, pp. 549, 552.
- ^ a b c Hinsley 1981, p. 206.
- ^ Bishop 2012, p. 73.
- ^ a b Kemp 1999, p. 29.
- ^ a b Kemp 1999, p. 30.
- ^ Woodman 2004, p. 70.
- ^ Sweetman 2000, p. 19.
- ^ a b Bishop 2012, p. 75.
- ^ Woodman 2004, pp. 73, 75.
- ^ Hinsley 1981, p. 207.
- ^ a b Roskill 1956, p. 121.
- ^ a b c Hinsley 1981, p. 208.
- ^ a b Bishop 2012, p. 76.
- ^ Zetterling & Tamelander 2009, p. 32.
- ^ Woodman 2004, p. 74.
- ^ a b Hinsley 1981, p. 209.
- ^ Bishop 2012, pp. 76–77.
- ^ Woodman 2004, p. 75.
- ^ Zetterling & Tamelander 2009, pp. 34–35.
- ^ a b Kemp 1999, p. 33.
- ^ a b c d Woodman 2004, p. 77.
- ^ a b c Hinsley 1981, p. 210.
- ^ Bishop 2012, p. 77.
- ^ a b c Bishop 2012, p. 78.
- ^ a b Bishop 2012, p. 79.
- ^ Kemp 1999, p. 34.
- ^ Zetterling & Tamelander 2009, p. 39.
- ^ Bishop 2012, pp. 79, 83.
- ^ Bishop 2012, p. 80.
- ^ a b Bishop 2012, p. 81.
- ^ a b c Bishop 2012, p. 82.
- ^ Rohwer 2005, p. 149.
- ^ Bishop 2012, pp. 82–83.
- ^ a b c Konstam 2018, p. 40.
- ^ Bishop 2012, p. 83.
- ^ a b Woodman 2004, p. 80.
- ^ a b Woodman 2004, p. 76.
- ^ Zetterling & Tamelander 2009, pp. 43–44.
- ^ Woodman 2004, pp. 80–81.
- ^ Bishop 2012, pp. 83–84.
- ^ Bishop 2012, p. 104.
- ^ a b c Roskill 1956, p. 123.
- ^ Faulkner 2012, p. 108.
- ^ Blair 2000, p. 549.
- ^ a b Kemp 1999, p. 35.
- ^ a b Bishop 2012, p. 84.
- ^ Roskill 1978, p. 132.
- ^ Kennedy 1979, p. 56.
- ^ Roskill 1956, p. 135.
- ^ a b Dimbleby 2015, p. 288.
- ^ Bishop 2012, p. 130.
- ^ Roskill 1956, p. 127.
- ^ Bishop 2012, p. 131.
- ^ Konstam 2018, p. 48.
- ^ Roskill 1956, p. 138.
- ^ a b Konstam 2018, p. 49.
- ^ Bercuson & Herwig 2002, p. 311.
- ^ Roskill 1956, p. 142.
- ^ Bennett 2012, pp. 11–21.
Bibliography[edit]
- Barber, Mark (2008). The British Fleet Air Arm in World War II. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-84603-283-7.
- Bennett, G. H. (2012). "Introduction". In Bennett, G. H. (ed.). Hunting Tirpitz: Naval Operations Against Bismarck's Sister Ship. Plymouth, Devon: University of Plymouth Press. pp. 7–25. ISBN 978-1-84102-310-6.
- Bercuson, David J.; Herwig, Holger H. (2002). Bismarck. London: Hutchinson. ISBN 978-0-09-179516-0.
- Bishop, Patrick (2012). Target Tirpitz. London: Harper Press. ISBN 978-0-00-743119-9.
- Blair, Clay (2000). Hitler's U-boat War: The Hunters 1939–1942. London: Cassell. ISBN 978-0-304-35260-9.
- Brown, David (2009). Hobbs, David (ed.). Carrier Operations in World War II. Barnsley, South Yorkshire: Frontline. ISBN 978-1-84832-042-0.
- Chesneau, Roger, ed. (1980). Conway's All The World's Fighting Ships 1922–1946. London: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 978-0-85177-146-5.
- Correll, John T. (22 December 2017). "In Pursuit of the Bismarck". Air Force Magazine. Retrieved 7 August 2021.
- Dimbleby, Jonathan (2015). The Battle of the Atlantic: How the Allies Won the War. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-241-97210-6.
- Faulkner, Marcus (2012). War at Sea: A Naval Atlas, 1939–1945. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-59114-560-8.
- Hinsley, F. H.; et al. (1981). British Intelligence in the Second World War: Its Influence on Strategy and Operations. Volume Two. History of the Second World War. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office. ISBN 978-0-11-630934-1.
- Kemp, Paul (1999). Convoy! Drama in Arctic Waters. London: Brockhampton Press. ISBN 978-1-86019-969-1.
- Kennedy, Ludovic (1979). The Death of the Tirpitz. Boston: Little, Brown and Company. ISBN 978-0-316-48905-8.
- Konstam, Angus (2018). Sink the Tirpitz 1942–44: The RAF and Fleet Air Arm Duel with Germany's Mighty Battleship. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-4728-3159-0.
- Konstam, Angus (2021). Big Guns in the Atlantic: Germany's battleships and cruisers raid the convoys, 1939–41. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-4728-4596-2.
- Rohwer, Jürgen (2005). Chronology of the War at Sea: 1939–1945: The Naval History of World War Two (Third revised ed.). Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-59114-119-8.
- Roskill, Stephen W. (1956). The War at Sea 1939–1945. Volume II: The Period of Balance. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office. OCLC 633635983.
- Roskill, Stephen W. (1978). Churchill and the Admirals. New York City: William Morrow and Company. ISBN 978-0-688-03364-4.
- Sweetman, John (2000). Tirpitz: Hunting the Beast. Air Attacks on the German Battleship, 1940–44. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-55750-822-5.
- Woodman, Richard (2004). The Arctic Convoys: 1941–1945. London: John Murray. ISBN 978-0-7195-6617-2.
- Zetterling, Niklas; Tamelander, Michael (2009). Tirpitz: The Life and Death of Germany's Last Super Battleship. Philadelphia: Casemate. ISBN 978-1-935149-18-7.
- Arctic convoys of World War II
- Arctic naval operations of World War II
- Naval battles and operations of World War II involving the United Kingdom
- Military operations of World War II involving Germany
- World War II aerial operations and battles of the Western European Theatre
- 1942 in Norway
- Conflicts in 1942
